
As someone deeply immersed in cloud infrastructure security, we understand how a single vulnerability can expose an entire system to significant risk. Recently, a severe security flaw has been discovered in the NVIDIA Container Toolkit, tracked as CVE-2024-0132, that impacted 100K+ substantial risk to cloud environments using containerized workloads. If successfully exploited, this vulnerability could allow attackers to break free from container restrictions and gain complete access to the underlying host system.
“Nvidia is a software and fabless company which designs and supplies graphics processing units (GPUs), application programming interfaces (APIs) for data science and high-performance computing, as well as system on a chip units (SoCs) for the mobile computing and automotive market.”
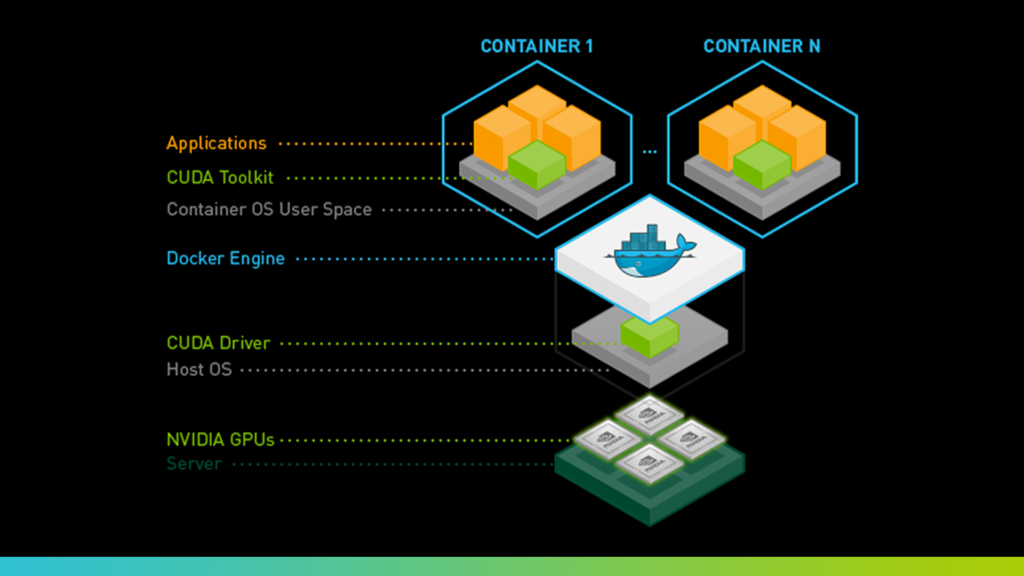
With a CVSS score of 9.0 out of 10, the vulnerability has been acknowledged in NVIDIA’s advisory, which states that it affects all versions of the NVIDIA Container Toolkit up to and including v1.16.1, and the NVIDIA GPU Operator up to 24.6.1. NVIDIA has addressed this issue in the recently released v1.16.2 和 24.6.2 versions.
Technical Details of the Vulnerability
The flaw is rooted in a Time-of-Check Time-of-Use (TOCTOU) vulnerability when the toolkit is used with its default configuration. This flaw could allow a specially crafted container image to gain access to the host file system, which can lead to dire consequences, including:
- Code execution
- Denial of service
- Escalation of privileges
- Information disclosure
- Data tampering
The implications are particularly severe in multi-tenant environments like Kubernetes, where a single compromised container could allow an attacker to access shared data, secrets, and control systems belonging to other applications running on the same node or cluster.
Hypothetical Attack Scenarios
Cybersecurity firm Wiz, which discovered and reported the vulnerability to NVIDIA on September 1, 2024, outlined a potential attack scenario. An attacker could create a rogue container image that, when executed on the target platform, grants them full access to the host file system. This could occur through a supply chain attack, where the victim is tricked into running the malicious image, or through services that permit shared GPU resources.
Once an attacker gains access, they can interact with Container Runtime Unix sockets (such as docker.sock or containerd.sock), which would allow them to execute arbitrary commands on the host system with root privileges, effectively taking control of the machine.
Recommended Actions
Given the critical nature of this vulnerability, it is highly recommended that all users apply the available patches immediately to mitigate potential threats. NVIDIA emphasizes that users utilizing Container Device Interface (CDI) configurations are not affected by this issue.
While there’s a growing focus on futuristic AI-based attacks, researchers remind us that “old-school” infrastructure vulnerabilities within the expanding AI tech stack pose immediate risks that security teams should prioritize and address.
結論
The CVE-2024-0132 vulnerability serves as a stark reminder of the importance of maintaining strong end-to-end security measures for cloud environments, especially as more organizations leverage AI workloads. Act now and secure your cloud infrastructure environment with Boyang (ToncentSoft). We provide real-time security solutions specifically cloud infrastructure, enabling organizations to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities efficiently. Contact us for FREE security audit and consultation to outsource the best security team from China or Vietnam for your company.
覺得這篇文章有趣嗎?請在 LinkedIn、, Twitter、 和 Facebook, 上支持我們,閱讀更多精彩內容。