Network security is a top priority for every business and individual due to the rapid adoption of advanced technologies where cybercrime is also increasing. On this stage, there are still 47% of businesses that don’t allocate any funds towards Network and cybersecurity. While, 51% of small businesses don’t utilize any IT security measures. 36% of small businesses never concern whatsoever about threats. Protecting sensitive data and critical applications from unauthorized access is very important to prevent network security threats. To protect your network effectively, you must first understand the various network security threats and vulnerabilities that could expose your systems to cyberattacks.
What is Network Security Threats?
Network security vulnerabilities refer to weaknesses in hardware or software that cybercriminals can exploit. These vulnerabilities might include outdated software, unpatched systems, or weak configurations that expose your network to potential breaches.
On the other hand, network security threats are specific attack methods used by hackers to exploit those vulnerabilities. Understanding both is essential for creating an end-to-end secure infrastructure.
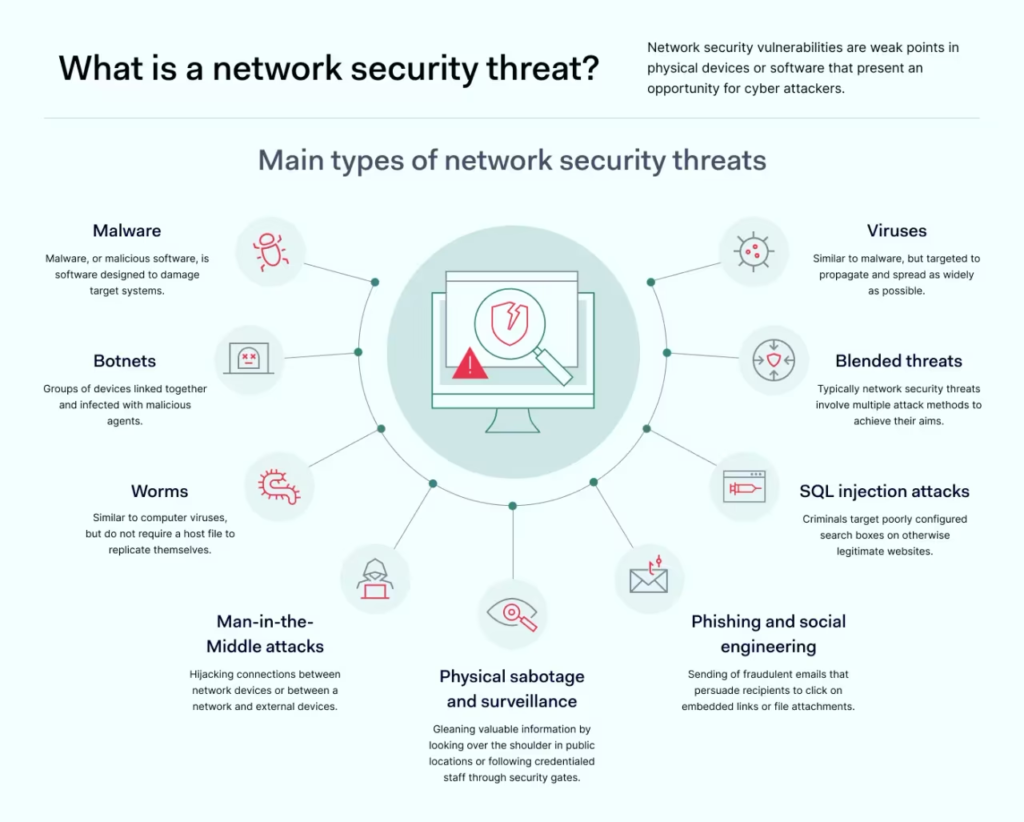
Types of Network Security Threats
- Malware Attack: Malware is a type of malicious software that infiltrates systems to damage, steal, or corrupt data. Common forms of malware include viruses, worms, trojans, and ransomware. Most malware infections result from phishing attacks or unpatched systems.
- Keyloggers Attack: Keyloggers record keystrokes, making it easy for attackers to steal login credentials or financial details. These are often difficult to detect, especially if installed deep within the operating system.
- Trojans Attack: Trojans disguise themselves as legitimate software, tricking users into downloading them. Once installed, they provide attackers access to the target system, leading to data theft or backdoor access for future attacks.
- Ransomware Attacks: Ransomware locks users out of their devices or files, demanding a ransom to restore access. This form of attack can cause significant financial loss, and paying the ransom doesn’t guarantee recovery.
- Adware and Spyware Adware forces users to view unwanted ads, while spyware gathers information such as browsing history or financial data, often without the victim’s knowledge.
- Computer Worms & Virus Attacks: Viruses attach themselves to files and spread through emails or downloads. Worms, however, do not need a host file and replicate rapidly across networks, making them difficult to contain.
- Botnets Botnets are groups of infected devices controlled by hackers to carry out large-scale attacks like Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS). These attacks can cripple websites by flooding them with traffic.
- Phishing Attack: Phishing attacks trick users into clicking malicious links or revealing sensitive information through fraudulent emails.
- Social Engineering Attack: manipulates individuals into breaking security protocols, exposing the network to breaches is called social engineering attack.
Reason of Network Vulnerability?
There are several reasons of Networks vulnerabilities, as follow:
- Legacy Software: Unpatched systems and outdated applications provide easy entry points for attackers.
- Misconfigurations: Weak passwords, poor access controls, or incorrectly configured firewalls expose sensitive data.
- Insider Threats: Employees, whether through negligence or malicious intent, can compromise network security.
- Insecure Devices: The rise of remote work and the use of Internet of Things (IoT) devices have expanded the attack surface, often through unsecured endpoints.
How to Identify and Mitigate Network Vulnerabilities
- Update Software Regularly Apply patches and updates to fix vulnerabilities in your operating systems and applications as soon as they are available.
- Ensure Network Visibility Use network monitoring tools to track traffic and detect unusual activity, helping identify potential threats before they cause significant damage.
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) ensures that even if passwords are compromised, attackers need an additional layer of security to access systems.
- Train Employees on Security Best Practices Regular training on identifying phishing emails and using secure connections can significantly reduce insider threats.
- Use Strong Perimeter Protections Firewalls, VPNs, and encryption tools provide the first line of defense by securing the outer edges of your network.
- Deploy Advanced Security Tools Use antivirus, anti-malware, and intrusion detection systems (IDS) to detect threats and prevent malware from spreading within your network.
- Regular Security Audits Conduct regular vulnerability assessments, penetration testing, and security audits to identify and address weak points in your network.
Take Away:
Understanding the importance of online security is an important part of every business for network security threats and vulnerabilities. By educating employees on cybersecurity best practices, misconceptions of cybersecurity and implementing best business security practices, you can reduce the risk of breaches. Proactive network security measures help ensure your organization’s data security 和 business continuity.
Remember, “the cost of prevention is always less than the cost of failure.” 立即聯繫我們, for FREE security audit and mitigat network & cybersecurity risks for your business.
Did you find this article helpful? Support on your favorite social platform LinkedIn、, Twitter、 和 Facebook, or subscribe our newsletter for more compelling content.