The rapid growth of technological advancement is increasing on the other hand protecting data and networks is becoming more critical than ever. Traditional security models assume a trusted internal network and focus heavily on defending the perimeter. However, with more people working remotely and accessing resources from multiple devices, these models often fall short. Enter Zero Trust Security, a modern approach of cyber security that assumes no implicit trust anywhere, constantly verifying and validating each access request.
This article will explain What is Zero Trust? The principles and the best security strategies that will help with data security and systems against advanced vulnerabilities.
What is Zero Trust?
Zero Trust is a security framework that requires strict identity verification for everyone and everything trying to access resources on a network, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the network perimeter. The idea behind is simple: “never trust, always verify.” By adopting Zero Trust principles, organizations ensure that access is only granted after a thorough verification process, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches.
Unlike traditional security models, which often rely on a single firewall or perimeter to protect the network, Zero Trust takes a layered, holistic approach. It uses a variety of methods to continuously verify and control access, making it adaptable to complex, cloud-based, and hybrid environments.
Key Principles of Zero Trust Security
To fully understand, let’s look at its fundamental principles, each of which plays a vital role in building a resilient and secure infrastructure.
1. Continuous Verification
Continuous verification is at the heart of Zero Trust. Unlike traditional models that may only verify credentials once at login, it involves verifying and authenticating at each access attempt, taking into account all available data points such as device, location, and user behavior. This ensures that no device, zone, or user is ever fully “trusted.” With continuous verification, access is only permitted if the request meets stringent security conditions.
2. Least Privilege Access
The principle of least privilege limits user access to only the resources they need to perform their tasks. By employing a “just-in-time” and “just-enough-access” approach, Zero Trust minimizes exposure to sensitive data and reduces the potential damage from a compromised account. For example, a user might receive access to a certain file or system only for a specific time, reducing the window for unauthorized activity.
3. Risk Mitigation with Dynamic Adjustments
Zero Trust security frameworks are designed to dynamically assess and adjust access levels based on risk. If a user’s risk level changes perhaps due to suspicious login locations or unusual activities the system may restrict access or prompt additional authentication. This ensures that security is adaptive and can respond immediately to potential threats, preventing access when risk indicators are high.
4. Automated Monitoring and Threat Detection
Automated monitoring plays a vital role in identifying potential threats and preventing unauthorized access. Zero Trust systems continuously monitor user behavior and device status to detect anomalies that may indicate a security risk. This approach, which combines automation with advanced analytics, allows organizations to gain real-time visibility into user activities across the network, flagging any suspicious or unauthorized actions for immediate investigation.
5. End-to-End Encryption
Zero Trust requires end-to-end encryption of data both in transit and at rest to protect against interception or tampering. Encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted, it cannot be read or misused. This level of security is especially important for protecting sensitive data transmitted between users, devices, and applications within a Zero Trust network.
6. Analytics for Visibility and Defense Improvement
Analytics are essential in for understanding user behaviors, detecting unusual activities, and continuously improving security measures. By using analytics, organizations can gain deeper visibility into network traffic, detect threats more quickly, and fine-tune defenses. Advanced data analysis also helps with proactive threat detection and response, enhancing the overall security posture.
7. Defense-in-Depth Strategy
Zero Trust follows a defense-in-depth approach, meaning it does not rely on a single security measure. Instead, it layers multiple security protocols and controls, such as authentication, monitoring, and access management, to safeguard assets. This layered security approach makes it harder for attackers to compromise the system and ensures there are multiple lines of defense in place.
8. Dynamic Policy Model Deployment
In a Zero Trust environment, policies should be flexible and scalable, enabling swift responses to new threats or changes in the IT environment. A dynamic policy model allows security teams to deploy and update access policies rapidly. This scalability ensures that even as the network grows or changes, the Zero Trust framework can adapt without sacrificing security.
9. Identity Threat Detection and Response
Identity threat detection and response is a critical element of Zero Trust that involves continuously monitoring for any indicators of identity compromise. By focusing on identity threats, organizations can detect compromised accounts early and take corrective action to prevent unauthorized access. This proactive approach is especially valuable in identifying and mitigating risks associated with credential theft and phishing attacks.
Best Zero Trust Security Strategy
Beyond these zero trust core principles, Zero Trust incorporates several other tactics that strengthen its framework:
- Microsegmentation: Divides the network into smaller segments to limit access to sensitive data, reducing the impact of any potential breach.
- Preventing Lateral Movement: Prevents unauthorized movement within the network by continuously verifying user identity and restricting access to only necessary areas.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Requires users to confirm their identity using multiple factors, such as passwords, biometrics, or access tokens that expire quickly.
- Device Access Control: Ensures that only authorized and compliant devices can access network resources.
- Workforce Security: Focuses on protecting employee identities and access, critical for preventing insider threats and unauthorized access.
- Workload Security: Safeguards application workloads in cloud and on-premise environments, essential for modern hybrid infrastructures.
- Data Security: Ensures data protection through policies that govern access, encryption, and monitoring, especially vital for compliance with regulations.
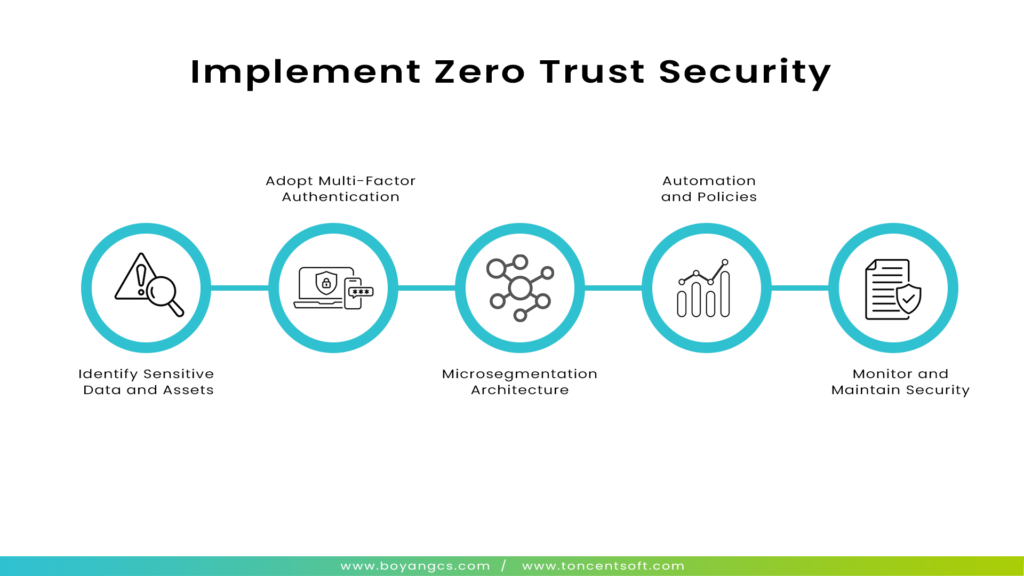
How to Implement Zero Trust Security?
If you are seeking to implement zero trust security that will involve a structured approach of 5 steps to implement zero trust include evaluating existing assets, defining access policies, and adopting advanced technologies. Key steps to include:
- Identify Sensitive Data and Assets: Start by mapping and classifying all sensitive assets and data to understand where Zero Trust policies are most critical.
- Adopt Multi-Factor Authentication: Implement MFA as a baseline to ensure secure user access.
- Use Microsegmentation: Break the network into smaller, manageable zones to contain any potential breach.
- Leverage Automation and Analytics: Use automated monitoring and data analytics to detect anomalies and flag potential threats in real time.
- Establish a Dynamic Policy Framework: Implement adaptive policies that allow rapid updates and adjustments based on emerging threats or changes in network conditions.
Wrap-up
Zero Trust is an adaptable approach of cyber security to ensure modern digital environments are secured. By focusing on strict identity verification, continuous monitoring, and a layered defense-in-depth strategy, it provides an end-to-end framework that goes beyond traditional security models. This approach not only minimizes the risk of breaches but also prepares organizations to respond dynamically to evolving cyber threats. Contact us to get a free security audit or consultation with our top network and cybersecurity experts to identify vulnerabilities and strengthen your critical infrastructure.
Found this article interesting? Support us on LinkedIn, Twitter and Facebook to read more compelling content.